Understanding Fibroids: Symptoms & Treatment Options
Understanding Fibroids
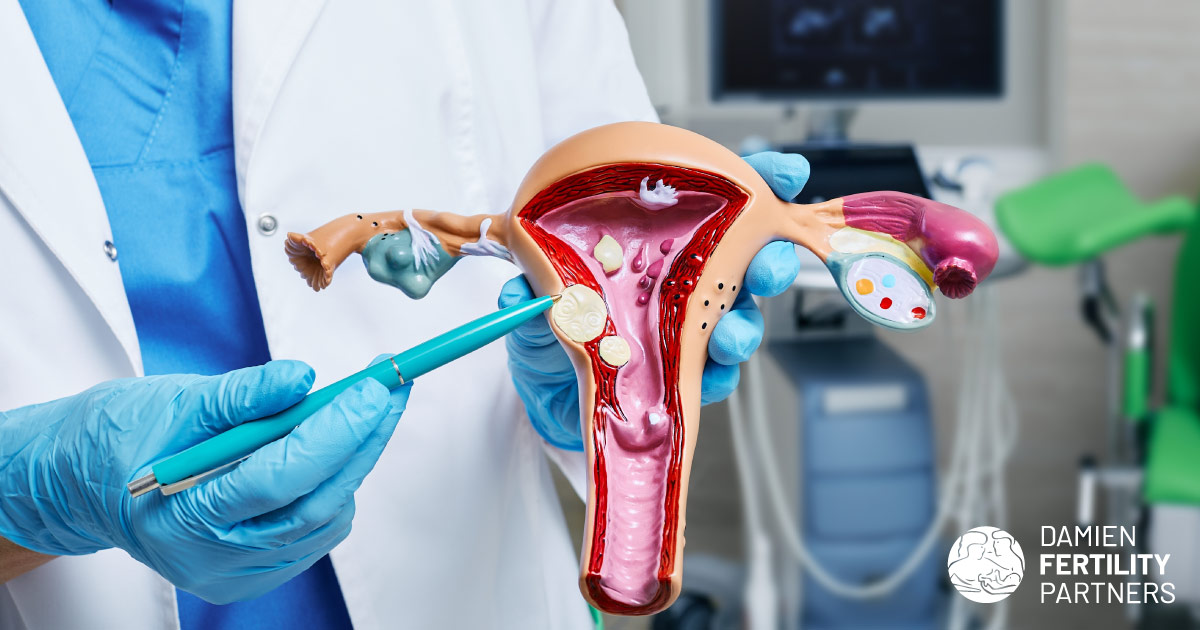
Fibroids are a prevalent cause of irregular vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain; they can contribute to miscarriages or infertility depending on their location. They are classified into three types: submucosal (inside the uterine cavity), intramural (within the uterine wall), or serosal (on outer surface of uterus). These benign tumors arise from the smooth muscle cells of the uterus and rarely transform into malignant sarcomas. They can range in size from as small as a pea to as large as a 30-week fetus. While their size is significant, their location is the most critical factor in determining symptoms and guiding treatment options. Ultrasound remains the most commonly employed method for their diagnosis and management.
Symptomatology and Impact on Fertility
Fibroids can induce symptoms such as pelvic pain, heavy and irregular bleeding, urinary frequency or urgency, and other gastrointestinal disturbances. Both the size and location of fibroids significantly influence the variety of symptoms. Dyspareunia, or pain during sexual intercourse, is also common with specific types of fibroids.
Our guiding principle for assessing the impact on infertility is the mantra: “location, location, location.” If a fibroid disrupts the endometrial lining, it can lead to miscarriages and hinder implantation, often resulting in more severe bleeding issues. Intramural fibroids may not necessitate intervention unless there is a concern that their growth during pregnancy could promote premature labor or loss of the pregnancy. Serosal fibroids can cause pain. This is due to pressure and “rubbing” other surfaces in the pelvis. Increased tubal adhesions can occur, which may indirectly cause infertility. These factors and symptoms typically guide the treatment approach.
Treatment Options
If fertility is not a goal, removal or ablation techniques can be utilized. Common methods include embolization of the fibroids through catheters directed to the uterine arteries, or the use of high-frequency ultrasound, causing the fibroids to shrink and halt their growth. This can alleviate pain and bleeding issues but will compromise fertility. Physicians may prescribe medications that induce a temporary menopausal state in women to shrink fibroids temporarily, most commonly with the drug Depo-Lupron. Although this approach effectively relieves symptoms, it is not a long-term solution as the fibroids will regrow once the treatment ceases.
Surgical Interventions and Fertility Considerations
For those desiring conception, and where fibroids impede success, hysteroscopy is an excellent method for removing submucosal fibroids. This technique demands a high level of surgical expertise. Laparoscopy or robotic laparoscopy are suitable methods for removing serosal or intramural fibroids. This technique is limited by the surgeon’s ability to effectively repair the uterine wall post-myomectomy. If pregnancy is desired the integrity of the repair is critical. For extensive fibroids that cannot be removed by laparoscopy, a laparotomy (an abdominal incision) is effective.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Fibroids stem from a genetic mutation frequently involving chromosome 12. These mutations may be identified in the fibroids themselves, though they typically do not affect the normal uterine smooth muscle cells. An underlying genetic predisposition or a specific mutation in a smooth muscle cell can initiate fibroid development. Vitamin D has been linked to reduced growth rate of fibroids, and maintaining adequate levels of this vitamin may help in preventing their development. Interestingly, fibroids are more common in women with darker skin tones, a phenomenon historically attributed to genetic factors. However, the correlation with Vitamin D, synthesized through sun exposure, suggests an alternative explanation.
Comprehensive Fertility Evaluation at Damien Fertility Partners
In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, patients with fibroids can experience severe pain and bleeding, leading to significant complications such as anemia and the potential need for emergency blood transfusions. During pregnancy, the risks of second-trimester loss, placental abruption, fetal growth restriction, and preterm birth are crucial considerations.
The evaluation of fibroids and their role in infertility is a critical component of fertility assessment. Initially, we perform a vaginal ultrasound to identify ovarian or uterine masses and cysts. This enables us to determine their location and size and assess their potential impact on infertility or other symptoms. At Damien Fertility Partners, our goal is to comprehensively evaluate both the individual and the couple. Our evaluations for infertility encompass hormonal issues, egg quality, semen analysis, tubal abnormalities, and other pelvic factors. Reproductive endocrinologists and infertility specialists are ideally suited to diagnose and address fertility issues. Our team is dedicated to enhancing and preserving your fertility, equipped with the necessary resources and expertise to address this significant medical challenge comprehensively.
Do you have questions and want to learn more? For guidance and support, contact Damien Fertility Partners at 732-758-6511 or hello@damienfertilitypartners.com.